Mentax
"Generic mentax 15 gm on-line, antifungal for nails".
By: M. Frillock, M.S., Ph.D.
Associate Professor, Idaho College of Osteopathic Medicine
Purchase mentax 15 gm without a prescription
Also fungus gnats larvae cannabis buy mentax 15gm low price, with posterior dislocation of the hip antifungal oral gel order discount mentax line, a high variety of transient or permanent sciatic nerve palsies could also be expected fungus jelly mentax 15 gm amex. Central instability could occur when the quadrilateral plate is large enough to permit the femoral head to sublux centrally fungus the bogeyman cheap 15 gm mentax. In such instances, some form of medial buttress is essential, both a spring plate or cerclage wire. Large anterior wall fragments, both in isolation with an related anterior dislocation (A3) or with an anterior with posterior hemitransverse pattern (B3) could also be large enough to permit anterior hip instability and require operative treatment. Incongruity the word incongruity comes from the Latin congruus to fit precisely; therefore incongruity means lack of an exact fit. All major joints require congruity for good lengthy-time period function, or secondary osteoarthritis will result. This is much more necessary with submit-traumatic joints, since direct articular change is added to the incongruity. Obviously, perfect anatomical discount restoring normal anatomy is the best, but this is probably not attainable in all instances. Clinical significance of an incongruous fracture depends on many factors, including the placement of the fracture, especially on the superior dome. Also, the size of the gap or more significantly, the size and site of the step is necessary. Unstable Hip Instability of the hip is most typical in posterior varieties but can also be current with a big free fragment of the quadrilateral plate or in anterior varieties with anterior wall fracture. If the posterior lip of the acetabulum is significantly displaced, permitting instability of the hip joint, open Table thirteen. Operative indications: fracture factors (from Tile 2003) Hip unstable and/or incongruous Guidelines to be correlated to affected person factors A. Fractures by way of the roof of the dome a) Displaced dome fragment b) Transverse or T varieties (transtectal) c) Both-column varieties with incongruity (displaced posterior column) 2. Soft tissue interposition Displacement of the Weight-Bearing Dome Displaced Dome Fractures. The hip was grossly unstable and the fracture dislocation required operative fixation. The obturator indirect view (c) and iliac indirect view (d) present the big posterior wall fragment (white arrows) and the transverse nature of the fracture. A typical large triangular fragment involving the dome portion of articular cartilage could also be displaced and even rotated 90°, as shown in. Open discount and inner fixation are essential to restore the anatomical relationship of that fragment to the remainder of the hip joint. These shearingtype accidents involving the superior portion of the dome are extremely difficult to scale back by closed means. With dislocation of the femoral head, large bone fragments could also be avulsed, usually with an intact teres ligament. This type of damage could occur with a pure dislocation or with a concomitant acetabular fracture. If the top fragment is large enough to trigger instability of the hip joint or is displaced enough to trigger incongruity, it must be restored anatomically and stuck with screws. Occasionally, the posterior capsule could interpose between the femoral head and the acetabulum during discount of a dislocation or could forestall discount, both indications for operative care. The growth of a sciatic or femoral nerve palsy after discount of the acetabular fracture, indicating the attainable entrapment of the nerve at discount. The presence of a femoral arterial damage associated with an anterior column fracture of the acetabulum. In this circumstance, the fracture must be fastened at the time of main vascular repair. Fracture of the ipsilateral femur, which makes closed treatment of the acetabulum nearly impossible; open discount is therefore indicated for both the fractured femur and the acetabular fracture (see. Patient Factors After full consideration of the fracture factors, the ultimate determination regarding open versus closed treatment depends on the affected person factors. Clearly, the younger the affected person assuming a sign for operative care, the more the surgeon ought to attempt for anatomical open discount and inner fixation. Large retained bone fragments throughout the acetabulum could act as a block to anatomical discount or could forestall normal biomechanical function of the joint.
Generic mentax 15 gm on-line
Governmental coverage National or state coverage emphasizing the necessity to fungus gnats fruit flies discount mentax 15 gm line alleviate chronic most cancers pain through training fungi vs parasite cheap mentax 15gm line, drug availability antifungal body wash walmart cheap 15gm mentax with amex, and governmental support/endorsement fungus gnats lemon juice quality 15 gm mentax. The coverage can stand alone, be a part of an overall national/state most cancers management program, be a part of an overall coverage on care of the terminally ill, or be a part of a coverage on chronic intractable pain. Education Public well being-care professionals (doctors, nurses, pharmacists), others (well being care coverage makers/administrators, drug regulators) Drug availability Changes in well being care laws/legislation to enhance drug availability (particularly opioids) Improvements within the space of prescribing, distributing, allotting, and administering medicine Guide to Pain Management in Low-Resource Settings Chapter forty three Resources for Ensuring Opioid Availability David E. The availability of opioid analgesics is dependent upon the system of drug management laws, laws, and distribution in your nation. Unless this method is able to safely distribute controlled medicines based on medical wants, clinicians shall be unable to use opioid analgesics to relieve reasonable to severe pain based on international well being and regulatory pointers and standards of modern drugs. This chapter poses numerous questions which might be relevant to a better understanding of how the system is meant to perform, and to determine and take away impediments to availability of opioids and affected person access to pain aid. Opioids may be helpful to deal with patients with chronic pain from noncancer conditions, but the choice of therapies must be made on a person foundation, ruled by a cautious consideration of risks and advantages of remedy. Case 1 A affected person was initially given radiotherapy for her pain, however it was not efficient as the illness progressed. Next she was given a weak pain-relieving medication, but her pain continued to worsen. Finally, she returned to the doctor in excruciating pain requesting medication that would finish her life. She was given another weak pain medication along with antidepressants and sent home. Such conditions usually arose on account of the difficulties encountered when trying to acquire the required licences. At other instances, manufacturers of the 321 Guide to Pain Management in Low-Resource Settings, edited by Andreas Kopf and Nilesh B. In these emergencies, the clinic would resort to otherwise unethical and unacceptable cutback measures, applied in such a means in order to decrease the impact on patients and households. International agreements which might be binding on governments have acknowledged for decades that narcotic medicine, i. These instances demonstrate some of the causes and the human influence of unrelieved severe pain when access to opioid analgesics is blocked. Such conditions are tragic and never should be allowed to happen, but they do set the stage for this chapter that will describe numerous assets that can be used by well being professionals and government in low-resource settings, or wherever else, to enhance availability and affected person access to opioid analgesics corresponding to oral morphine. The following questions and responses are intended to assist clinicians and advocates of their efforts to enhance affected person access to pain aid. Readers are inspired to seek the advice of the resource materials referenced within the text and on the finish, refer to other chapters in this book, and seek skilled skilled guidance on specific questions referring to medical pharmacology, drugs, and legislation. What is the world scenario concerning the supply of opioids corresponding to oral morphine for people in pain? Clinicians understand only too well how unrelieved severe pain can destroy quality of life and generally even the desire to stay. Some-but not all-of the wealthier international locations have fairly good opioid availability, and therefore patients have access to opioid analgesics. Lack of access is very serious in settings with limited assets and an inadequate well being care infrastructure. While other chapters handle this question in more element, it is very important observe that a wide range of drug and nondrug therapies, together with surgical procedures, radiation, and behavioral strategies, may be helpful in treating pain and offering palliative care. Efforts to enhance opioid availability should be guided by the drug regulatory principle of "balance. Some opioids, corresponding to fentanyl, morphine, hydromorphone, and oxycodone can relieve reasonable to severe and escalating pain. These opioid agonists lack a "ceiling impact" in order that the dose may be increased to relieve rising pain, preserving in mind side effects. There is settlement that a number of opioid agonists in different dosage forms should be out there to allow clinicians to change opioids, doses, and routes of administration to maximize efficacy and decrease side effects. The aim is to ensure the supply of these important pain aid medicines at an affordable price, when and the place wanted by patients.
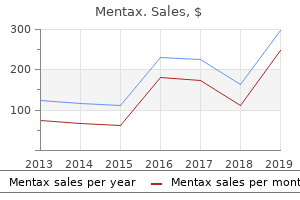
Discount mentax 15gm fast delivery
Human unipolar cells have an axon that emerges from the cell physique fungus on lips discount mentax 15 gm visa, however it splits so that the axon can lengthen alongside a really lengthy distance antifungal home remedies buy generic mentax on line. At one finish of the axon are dendrites antifungal meds order mentax 15 gm on-line, and at the different finish fungal nail salon discount mentax on line, the axon types synaptic connections with a target. Unipolar cells are solely sensory neurons and have two unique traits. First, their dendrites are receiving sensory info, typically directly from the stimulus itself. The axon tasks from the dendrite endings, previous the cell physique in a ganglion, and into the central nervous system. Bipolar cells have two processes, which lengthen from every finish of the cell physique, reverse to each other. They are discovered mainly within the olfactory epithelium (where smell stimuli are sensed), and as part of the retina. With the exception of the unipolar sensory ganglion cells, and the two specific bipolar cells mentioned above, all different neurons are multipolar. Neurons can also be functionally classified on the premise of the role they play within the nervous system. Sensory, or afferent, neurons carry information about the environment towards the central nervous system. Interneurons are discovered solely inside the central nervous system and obtain info either from sensory neurons or different interneurons. Motor, or efferent, neurons obtain info from interneurons or directly from sensory neurons so as stimulate responses in tissues throughout the physique. Describe the structural modifications that contribute to specific operate for every tissue type & sub-type 6. Virtual Microscope Skeletal Muscle (58Thin) Access a bit of skeletal muscle by following the hyperlink: 141. Virtual Microscope Smooth Muscle (one hundred fifty five) Access a bit of the gastro-esophageal junction by following the hyperlink: 141. Virtual Microscope Cardiac Muscle (98-1) Access a bit of the guts ventricle by following the hyperlink: 141. For every provided tissue slide, zoom in and determine a representative part showing the provided muscle tissue sub-type. Name & determine the connective tissue layers that wrap the components of muscle: deep fascia, epimysium, perimysium, and endomysium. Define and supply examples of the functional courses of muscle tissue: prime mover, synergist, antagonist, and fixator. List the connective tissue layers that surround skeletal muscle from superficial to deep. Describe the final anatomy of a nerve Required Materials None Procedure this activity will be accomplished individually or in small groups. Distinguish between the central and peripheral nervous systems by itemizing examples of unique buildings discovered within every division. For every given functional neuron class, list the structural type(s) of neurons usually discovered and summarize in a single sentence how that neuron construction contributes to operate. Your answer should include definitions of every and a quick assertion on how they differ. List and summarize a number of features of the integumentary system Distinguish between skinny and thick pores and skin based mostly on appearance, construction, and function Distinguish the epidermis from the dermis Identify and describe the layers of the epidermis and dermis Identify various accessory buildings of the integument on a mannequin or an image/diagram Background Information the integumentary system refers to the pores and skin and its accessory buildings, and is answerable for rather more than merely lending to your outward appearance. In the grownup human physique, the pores and skin makes up about sixteen p.c of physique weight and covers an area of 1. In truth, the pores and skin and accessory buildings are the biggest organ system within the human physique. The pores and skin and its accessory buildings make up the integumentary system, which carries out a number of features together with bodily protection, thermoregulation, serving as a serious sensory organ, taking part in a key role in your immune systems, and is a serious website of lipid storage. The pores and skin is manufactured from a number of layers of cells and tissues, which are held to underlying muscle tissue and different buildings by connective tissue (Figure 5. The deeper layer of pores and skin is well vascularized (has numerous blood vessels) and has numerous sensory buildings and nerve fibers to enable communication to and from the mind. The pores and skin consists of two major layers: the epidermis and the dermis which incorporates blood vessels, hair follicles, sweat glands, and different buildings. Beneath the dermis lies the hypodermis, which consists mainly of loose connective and fatty tissues.
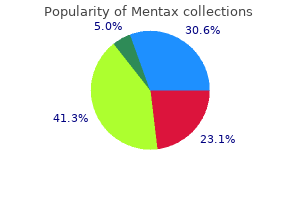
Best mentax 15gm
Postural Restoration management of a Female with Right Pelvic and Proximal Hamstring Pain antifungal herbs buy cheap mentax on line. Postural Respiration An Integrated Approach to Treatment of Patterned Thoraco-Abdominal Pathomechanics quercetin antifungal activity generic mentax 15 gm visa. The relation between organ anatomy and pre-existent vertebral rotation in the normal spine antifungal soap for jock itch discount mentax 15 gm overnight delivery. The efficacy of a treatment program focusing on specific stabilizing exercises for pelvic girdle pain after pregnancy: a two-year follow-up of a randomized clinical trial antifungal pill otc order generic mentax pills. A randomized clinical trial of manual versus mechanical force manipulation in the treatment of sacroiliac joint syndrome. Treatment and biochemical assessment of patients with chronic sacroiliac syndrome. Postural Restoration Management for Patients with Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction: A Case Series. Assessing disability and change on individual patients: a report of patient specific measure. Section one is about basic science, epidemiology, risk factors and evaluation, section two is about clinical science especially different approach in exercise therapy. I envisage that this book will provide helpful information and guidance for all those practitioners involved with managing people with back pain-physiotherapists, osteopaths, chiropractors and doctors of orthopedics, rheumatology, rehabilitation and manual medicine. Likewise for students of movement and those who are involved in re-educating movement-exercise physiologists, Pilates and yoga teachers etc. How to reference In order to correctly reference this scholarly work, feel free to copy and paste the following: Kyndall Boyle (2012). Conservative Management for Patients with Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction, Low Back Pain, Dr. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 3. Gluteal arteries Cutaneous lymphatic drainage- lateral group of superficial inguinal lymph nodes Deep fascia- above & in front of gluteus medius is thick but over gluteus maximus it is thin. The deep fascia splits & encloses gluteus maximus Muscles of gluteal region Muscles of gluteal region Gluteus maximus Gluteus maximus Nerve supply- inferior gluteal nerve Action- Extension of hip joint, also causes lateral rotation & abduction at this joint Acting from its insertionstraighten the trunk Prevents the pelvis from rotating forward on the head of femur Thru the iliotibial tract steadies the femur on tibia while standing Structures undercover gluteus maximus Muscles- glut. Medius & minimus,rectus femoris,(reflected head), Piriformis, obturator internus with two gemelli,Quadratus femoris,obturator externus, Origin of four hamstring from ischial tuberosity, Insertion of pubic fibers of ad. Femoral vessels, trochanteric & cruciate anastomosis Nerves-Superior gluteal, inferior gluteal, sciatic, Post. Nerve of thigh, nerve to quadratus femoris, pudendal nerve, nerve to obturator internus &perforating cutaneous nerves Bones & joints- ilium, ischial tuberosity, upper end of femur with greater trochanter, sacrum, coccyx, hip joint &sacroiliac joint Ligaments- sacrotuberous, sacrospinous & ischiofemoral Bursa- trochanteric bursa of glut. Medius & minimus is paralysed, patient sways on the paralysed side to clear the opposite foot off the ground. When bilateral the gait is called as waddling gait Trendelenburg test- normally when the body weight is supported on one limb, the glutei of the supported side raise the opposite (unsupported) side of the pelvis. However if abductor mechanism is defective, the unsupported side of the pelvis drops and this is known as positive trendelenburg test. The test is positive in defects of muscle, congenital dislocation of hip & ununited fracture of femur piriformis Nerve supply- direct branch from L5, S1&S2 Action- lateral rotator of femur Obturator internus Nerve supply-nerve to obturator internus Action- Lateral rotator of femur Gemelli Nerve supplysuperior gemelli by nerve to obturator internus, inferior gemelli by nerve to quadratus femoris Action- help in lateral rotation Quadratus femoris Nerve supply- nerve to quadratus femoris Action- lateral rotator of thigh Obturator externus Obturator nerve Action- Lateral rotator of femur Arteries Inferior gluteal arteryArtery of sciatic nerve Anastomotic br. Coccygeal artery Superior gluteal arterySuperficial branch Deep branch Internal pudendal artery Various anastomosis Arterial anastomosis in gluteal region Cruciate anastomosis- present in the lower part of the gluteal region. Arteries taking part are anastomotic branches of inferior gluteal artery, first perforating artery & transverse braches of lat. Taking part in anastomosis are descending branches of superior gluteal artery, ascending branch of medial & lateral cir. Femoral arteries Nerves in gluteal region Structures passing thru greater sciatic foramenPiriformis fills the foramen structures passing above the piriformis are- superior gluteal nerve and superior gluteal vessels Structures passing below the piriformis are-Inferior gluteal nerve, inferior gluteal vessels, sciatic nerve, posterior cutaneous nerve of thigh, nerve to quadratus femoris, pudendal nerve, internal pudendal vessels, nerve to obturator internus Structures passing thru lesser sciatic foramenpudendal nerve, Internal pudendal vessels, nerve to obturator internus, tendon of obturator internus Applied I/m injection is given in superolateral quadrant of gluteal region to avoid injury to nerves. Bone is best at withstanding compression, especially against the "grain" (compressing long axes of osteones) External Force Internal Force (Stress) Tensile strength = 1/2 of compression; comparable to tendons & ligaments Shear strength = 1/4 of compression; most fracture are the result of shear forces Internal Distortion (Strain) General Principle: Bones are designed to provide adequate strength with minimal material (minimal mass or weight). Asa result, passive muscles are able to serve as ties that reinforce joints & oppose forces on bones. Musclearenamed(originallyinthehuman)fortheirshape(deltoideus)orlocation(brachialis) or attachments (sternohyoideus) or structure (biceps) or function (supinator) or combinations of these(pronatorquadratus;superficialdigitalflexor;serratusventralis;flexorcarpiradialis;etc. Muscle architecture: Multiplemusclesandmultiplepartsorheads(head=aseparatebellyandorigin)existto distribute (as opposed to concentrate) stresses on bones and to provide movement diversity. This results in a greater range of shortening and thus yields greater movement velocity (distance per time).
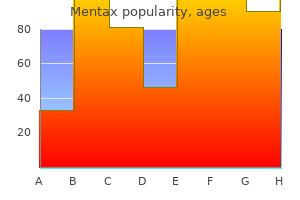
Order mentax with american express
This space is the positioning of articulation between the proximal radius and the ulna fungus gnats vegetable seedlings generic 15gm mentax with visa, forming the proximal radioulnar joint fungus gnats tea cheap 15 gm mentax with amex. The posterior and superior portions of the proximal ulna make up the olecranon course of antifungal yeast treatment 15gm mentax fast delivery, which varieties the bony tip of the elbow fungus gnats with no plants 15gm mentax sale. The ulna is situated on the medial aspect of the forearm, and the radius is on the lateral aspect. The lateral aspect of the shaft varieties a ridge called the interosseous border of the ulna. This is the road of attachment for the interosseous membrane of the forearm, a sheet of dense connective tissue that connects the ulna and radius bones. Projecting from the posterior aspect of the ulnar head is the styloid process of the ulna, a brief bony projection. This serves as an attachment point for a connective tissue construction that connects the distal ends of the ulna and radius. It permits the forearm and hand to swing freely or to carry an object without hitting the hip. The Radius the radius runs parallel to the ulna, on the lateral aspect of the forearm (Figure thirteen. The small melancholy on the surface of the pinnacle articulates with the capitulum of the humerus as part of the elbow joint, whereas the smooth, outer margin of the pinnacle articulates with the radial notch of the ulna on the proximal radioulnar joint. The neck of the radius is the narrowed region immediately beneath the expanded head. Inferior to this point on the medial aspect is the radial tuberosity, an oval-shaped, bony protuberance that serves as a muscle attachment point. The shaft of the radius is barely curved and has a small ridge along its medial aspect. This ridge varieties the interosseous border of the radius, which, like the same border of the ulna, is the road of attachment for the interosseous membrane that unites the two forearm bones. The distal end of the radius has a easy surface for articulation with two carpal bones to form the radiocarpal joint or wrist joint (Figure thirteen. This shallow melancholy articulates with the pinnacle of the ulna, which collectively form the distal radioulnar joint. The lateral end of the radius has a pointed projection called the styloid process of the radius. This offers attachment for ligaments that support the lateral aspect of the wrist joint. Compared to the styloid process of the ulna, the styloid process of the radius initiatives more distally, thereby limiting the range of motion for lateral deviations of the hand on the wrist joint. The Carpal Bones the wrist and base of the hand are fashioned by a sequence of eight small carpal bones (see Figure thirteen. The carpal bones are organized in two rows, forming a proximal row of 4 carpal bones and a distal row of 4 carpal bones. The bones within the proximal row, running from the lateral (thumb) aspect to the medial aspect, are the scaphoid ("boat-shaped"), lunate ("moon-shaped"), triquetrum ("three-cornered"), and pisiform ("peashaped") bones. The small, rounded pisiform bone articulates with the anterior surface of the triquetrum bone. The pisiform thus initiatives anteriorly, where it varieties the bony bump that can be felt on the medial base of your hand. The distal bones (lateral to medial) are the trapezium ("desk"), trapezoid ("resembles a desk"), capitate ("head-shaped"), and hamate ("hooked bone") bones. The hamate bone is characterised by a outstanding bony extension on its anterior aspect called the hook of the hamate bone. A useful mnemonic for remembering the association of the carpal bones is "So Long To Pinky, Here Comes the Thumb. This can be seen within the radiograph (X-ray image) of the hand that shows the relationships of the hand bones to the pores and skin creases of the hand (Figure thirteen. Within the carpal bones, the four proximal bones are united to one another by ligaments to form a unit. Only three of these bones, the scaphoid, lunate, and triquetrum, contribute to the radiocarpal joint. The scaphoid and lunate bones articulate directly with the distal end of the radius, whereas the triquetrum bone articulates with a fibrocartilaginous pad that spans the radius and styloid process of the ulna. The proximal and distal rows of carpal bones articulate with one another to form the midcarpal joint (Figure thirteen.
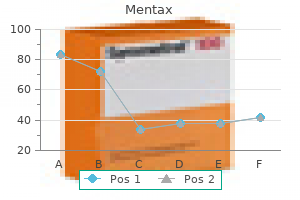
Paparaminta (Peppermint). Mentax.
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- Upset stomach (dyspepsia).
- Tension headaches when applied topically.
- Dosing considerations for Peppermint.
- Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), toothaches, itchy skin, infections, morning sickness, nausea and vomiting, painful menstrual periods, bacteria overgrowth in the intestines, lung infections, spasms of the stomach and gallbladder, cough and symptoms of cold, inflammation of mouth and respiratory tract lining, muscle or nerve pain, and other conditions.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96691
Generic 15 gm mentax free shipping
Colour: dirty brownish or yellowish fungus resistant fescue purchase cheap mentax on line, or a somewhat uniform colouring with out distinct pattern fungus how to get rid mentax 15gm sale. Habitat antifungal drugs buy 15gm mentax with amex, biology antifungal ear cream buy discount mentax on line, and fisheries: Occurring in depths between a hundred thirty and a pair of 047 m on muddy, sandy and onerous bottoms. Experimental fisheries around the Canary Islands confirmed massive numbers of crabs in numerous kinds of traps caught at depths between 550 and 1 200 m. Distribution: East Atlantic: Madeira, Canary Islands and Cape Verde Islands, alongside the Atlantic coast of Europe as far north as southwestern Norway. Remark: Genetic research show that the populations of the northwestern Atlantic commercially essential Chaceon quinquedens and the northeastern Atlantic populations of Chaceon affinis are very related. Brachyura: Eubrachyura: Heterotremata: Portunoidea: Geryonidae 305 Chaceon maritae (Manning and Holthuis, 1981) Frequent synonyms / misidentifications: None / Geryon quinquedens sensu Monod, 1956 (non S. Front with 4 short and broad enamel, no median tooth; anterolateral margin with 5 blunt, extensive, obscure enamel (outer angle of orbit included), of which the second and fourth are significantly vague. Chelipeds slightly unequal in form and size; final 4 pairs of legs equal or nearly so, smooth, with out hairs or spines; meri with out distal spine; dactyls dorsoventrally flattened. Size: Carapace of males to 14 cm lengthy and sixteen cm extensive, in the females these measurements are 8. Habitat, biology, and fisheries: Inhabits muddy bottoms between a hundred and 936 m depth; most frequent between 300 and 700 m. Taken by trawlers, but in areas the place the bottom is tough, exploratory fishing with traps met with cheap success. Marketed recent, but Spanish trawlers that catch the species as a bycatch to shrimps sell solely the chelipeds. Distribution: East Atlantic: Western Sahara and Canary Islands to Southwest Africa. Front with 4 poorly developed enamel, 2 median enamel extending little beyond outer 2 enamel, no median tooth; anterolateral margin with 3 acute enamel, the lateralmost being strongest. Chelipeds slightly unequal in form and size; final 4 pairs of legs equal or nearly so, smooth, with out hairs or spines; meri of fifth legs with out distal spine; dactyls dorsoventrally flattened. Habitat, biology, and fisheries: Recorded from delicate bottoms between 32 and 690 m, mostly deeper than a hundred m. Distribution: East Atlantic: Morocco and Canary Islands, alongside the Atlantic coasts of Europe as much as Norway. Last pair of legs with distal 2 segments wider and more flattened than these segments of previous legs, in most species the dactylus is oval and paddle-formed, tailored for swimming purposes, none of the dactyli with conspicuous spines. D anterolateral margin with 59 enamel segments 35 fused, immovable 5 4 male stomach segments 35 immovable final pair of legs paddle-like 3 male stomach Habitat, biology, and fisheries: Benthic to semipelagic crabs with diverse habits. In the Matutidae no less than the final 3 pairs of legs are paddle-like while in the Portunidae solely the final pair. Frontal margin of carapace with irregular incisions and with enamel of various sizes. Frontal margin of carapace with out median incision, triangular or straight, with out enamel. Carapace slightly broader than lengthy, granulose, with small ridges and transversal strains of granules; entrance with 2 undulations on both sides; small tooth current between 2 supraorbital fissures. Carapace as long as broad, smooth; entrance with 1 undulation on both sides; no small tooth between supraorbital fissures. Carapace subcircular, anterolateral enamel small; dactyli of second to fourth legs flattened, however not paddle-like as in fifth. Carapace hexagonal, anterolateral enamel nicely developed; dactyli of second to fourth legs styliform. Last anterolateral tooth on carapace larger than others, directed laterally; carapace coated with tubercles 8b. Fifth anterolateral tooth of carapaces slightly larger than previous 4; frontal margin with median tooth acute, not exceeding outward directed submedian enamel (Figs 7c and 8) 9b. Second anterolateral tooth of carapace smaller than third and fourth enamel (Figs 7a and 9) 10b. Second to fourth anterolateral enamel of carapace equal in size (Figs 7b and 10).
Purchase mentax 15 gm without a prescription. ATHLETES FOOT CURE DEFENSE SOAP RINGWORM IMPETIGOACNE STAPH TINEA VERSICOLOR.
Order mentax 15 gm otc
It incorporates the corpora quadrigemina fungus gnats how to get rid of naturally purchase mentax visa, concerned with visible and auditory reflexes fungus white spots buy mentax from india, and the cerebral peduncles topical antifungal yeast infection order mentax 15gm, composed of fiber tracts fungus gnat eggs order 15gm mentax with mastercard. Of these, the two upper eminences, the superior colliculi, are concerned with visible reflexes; the two posterior eminences, the inferior colliculi, are answerable for auditory reflexes. The red nucleus is grey matter that connects the cerebral hemispheres and the cerebellum. It features in reflexes concerned with motor coordination and sustaining posture. Another pigmented nucleus, the substantia nigra, is inferior to the red nucleus and is thought to inhibit involuntary actions. The metencephalon is the region of the brainstem that incorporates the pons and the cerebellum (see rvey fig. The pons consists of fiber tracts that relay impulses from one region of the mind to one other. Other nuclei of the pons, within the apneustic and pneumotaxic facilities, cooperate with nuclei within the rhythmicity area of the medulla oblongata to regulate the speed of breathing (fig. The two principal features of the cerebellum are to coordinate physique movement and to preserve steadiness. In order to carry out these features, the cerebellum is in fixed communication with different neurologic buildings via the cerebellar peduncles, that are fiber tracts that extend into and assist the cerebellum. Objective G Su To describe the situation and structure of the medulla oblongata and to state its features. Connected to the spinal wire and composing much of the brainstem, the medulla oblongata is rvey the principal structure inside the myelencephalon. The medulla oblongata incorporates nuclei for cranial nerves and very important autonomic features. The reticular formation, which arouses the cerebrum, is partially positioned within the myelencephalon. The medulla oblongata consists primarily of white matter within the form of descending and ascending tracts that talk between the spinal wire and various parts of the mind. Most of the projection fibers that type these tracts decussate, or cross to the opposite facet, via the pyramidal region of the medulla oblongata (see fig. The grey matter of the medulla oblongata consists of a number of essential nuclei (fig. Motor Nuclei Sensory Nuclei Accessory oculomotor Oculomotor Trochlear Trigeminal Abducens Facial Superior and inferior salivatory nuclei Hypoglossal Vagus Nucleus ambiguus Nucleus of spinal tract of trigeminal Accessory Mesencephalic nucleus of trigeminal Trigeminal Vestibular nuclei Dorsal and ventral cochlear nuclei Nucleus of tractus solitarius Figure 10. Both inhibitory fibers (via the vagus nerves) and accelerator fibers (via spinal nerves T1T5) come up from nuclei of the cardiac middle. Impulses from the vasomotor middle trigger the sleek muscles of arteriole walls to contract, thus raising the blood pressure. The fee and depth of breathing are managed by nuclei of this middle, along with those of the pons (see downside 10. In order from the outside in, these are the dura mater, the arachnoid, and the pia mater (see fig. The cranial dura mater is divided into a thicker periosteal layer and a thinner meningeal layer. In certain areas of the mind, the two layers of the cranial dura mater are separated to type enclosed dural sinuses that collect venous blood and drain it to the internal jugular veins of the neck. It incorporates loose fibrous and adipose connective tissues that type a protecting pad across the spinal wire. An epidural block is an injection of an anesthetic solution within the spinal wire region the place the spinal nerves pass via the epidural house. It is administered incessantly within the decrease lumbar area (between L3 and L4) to ladies in labor. By contrast, a spinal faucet (or lumbar puncture) administered in the same location punctures the dura mater.

Mentax 15 gm fast delivery
Rh 5 330 N Note: Both parts of the joint reaction pressure are directed through the joint heart fungus gnats infestation generic mentax 15 gm, and so have a moment arm of zero with respect to the middle of rotation fungus weed order 15 gm mentax visa. Fm R v Rh wt dwt Muscles that connect to the humerus at small angles with respect to the glenoid fossa contribute primarily to shear versus anti fungal immune response buy mentax 15 gm online compression at the joint antifungal uses generic 15gm mentax amex. These muscles serve the essential role of stabilizing the humerus within the glenoid fossa in opposition to the contractions of powerful muscles that might in any other case dislocate the joint. Maximum shear pressure has been found to be present at the glenohumeral joint when the arm is elevated roughly 60° (79). Because the vertical parts of muscle pressure largely cancel each other, the oppositely directed horizontal parts produce rotation of the humerus. Dislocations the glenohumeral joint is essentially the most generally dislocated joint within the body (6). The unfastened structure of the glenohumeral joint enables extreme mobility but provides little stability, and dislocations may occur in anterior, posterior, and inferior directions. The sturdy coracohumeral ligament usually prevents displacement within the superior path. Glenohumeral dislocations typically occur when the humerus is kidnapped and externally rotated, with anterior-inferior dislocations extra frequent than those in different directions. Factors that predispose the joint to dislocations embody inadequate size of the glenoid fossa, anterior tilt of the glenoid fossa, inadequate retroversion of the humeral head, and deficits within the rotator cuff muscles (67). Glenohumeral dislocation may outcome from sustaining a large external pressure during an accident, similar to in biking, or during participation in a contact sport similar to wrestling or football. Unfortunately, as soon as the joint has been dislocated, the stretching of the encircling collagenous tissues beyond their elastic limits generally predisposes it to subsequent dislocations. Individuals with this condition ought to strengthen their shoulder muscles earlier than athletic participation (24). Dislocations or separations of the acromioclavicular joint are additionally frequent amongst wrestlers and football players. When a rigidly outstretched arm sustains the pressure of a full-body fall, either acromioclavicular separation or fracture of the clavicle is more likely to outcome. Rotator Cuff Damage A frequent harm amongst employees and athletes who engage in forceful overhead movements typically involving abduction or flexion along with medial rotation is rotator cuff impingement syndrome, also called subacromial impingement syndrome, or shoulder impingement syndrome. This is the most common dysfunction of the shoulder, with progressive lack of perform and disability (fifty two). The trigger is progressive pressure on the rotator cuff tendons by the encircling bone and gentle tissue structures. This may end up in irritation of the underlying tendons and bursae or, in severe cases, rupture of one of the rotator cuff tendons. The muscle mostly affected is the supraspinatus, presumably because its blood supply is essentially the most vulnerable to pressure (sixty eight). This condition is accompanied by ache and tenderness within the superior and anterior shoulder areas, and typically by associated shoulder weak spot. The signs are exacerbated by rotary movements of the humerus, particularly those involving elevation and inside rotation. Activities that will promote the event of shoulder impingement syndrome embody throwing (particularly an implement like the javelin), serving in tennis, and swimming (particularly the freestyle, backstroke, and butterfly) (three, fifty nine, 72). Reports point out shoulder ache complaints in up to 50% of competitive swimmers (40). Older golfers additionally frequently develop impaired rotator cuff perform secondary to degenerative adjustments similar to osteophyte formation that impinges upon the subacromial house (four). Anatomical components believed to predispose an individual to impingement syndrome embody a flat acromion with only a small inclination, bony spurs at the acromioclavicular joint secondary to osteoarthritis, and a superiorly positioned humeral head (20, 63, 77). A number of theories have been proposed concerning the biomechanical causes of rotator cuff issues. The impingement concept suggests that a genetic issue results in the formation of too slim an area between the acromion process of the scapula and the pinnacle of the humerus. In this case, the rotator cuff and associated bursae are pinched between the acromion, the acromioclavicular ligament, and the humeral head each time the arm is elevated, with the resulting friction inflicting irritation and put on. An various concept proposes that the main issue is irritation of the supraspinatus tendon brought on by repeated overstretching of the muscletendon unit. Consequently, the deltoid muscles pull the humeral head up too high during abduction, leading to impingement and subsequent put on and tear on the rotator cuff. Research has proven that through the recovery phase of swimming, when the arm is elevated above the shoulder whereas being medially rotated, the serratus anterior rotates the scapula so that the supraspinatus, infraspinatus, and middle deltoid may freely abduct the humerus (fifty six).